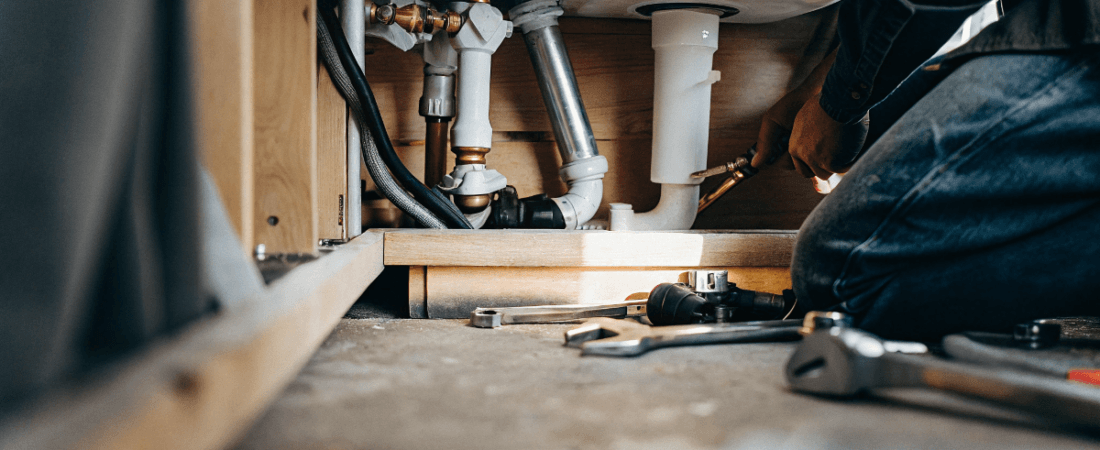
Ever wondered how does tiny house plumbing work?
I did too when I started my tiny house journey.
How do tiny homes deal with sewage?
What about water supply?
These are real concerns for tiny homeowners.
Let’s break it down.
Key Points:
- Understanding Tiny House Plumbing Basics: A tiny house plumbing system requires a water source, pipes, and drainage, with options for on-grid or off-grid setups, including rainwater collection.
- Unique Challenges of Tiny House Plumbing: Due to limited space and mobility, tiny house plumbing must be carefully planned and adaptable, with smaller components and considerations for space constraints.
- Designing an Efficient Plumbing System: Effective layout, proper sizing, and space-saving fixture placement are crucial to maximize space, ensure proper drainage, and meet water needs.
- Water Supply, Filtration, and Heating: Tiny houses can source water from city hookups, rain, or wells, with filtration systems like activated carbon or reverse osmosis, and use tankless or traditional heaters based on space.
- Drainage, Venting, and Climate Protection: Proper venting prevents odors and gases, while systems for greywater and blackwater, insulation, and heat tape help protect plumbing in extreme climates.
- Understanding Tiny House Plumbing Basics
- Designing an Efficient Plumbing System
- Water Supply and Management
- Heating Your Water
- Drainage, Venting, and Waste Disposal
- Choosing the Right Plumbing Materials
- Winterizing Your Plumbing
- DIY vs. Hiring a Pro
- Essential Tips for Maintenance
- Estimating Costs
- Protecting from Climate Challenges
- Final Thoughts
- FAQ's
Understanding Tiny House Plumbing Basics
Key Components
A tiny house plumbing system needs a water source, pipes, and a drainage system. There are generally two types of plumbing systems for tiny houses: on-grid and off-grid.
Water Source:
Hookup or water tank. Rainwater collection systems are a popular eco-friendly method for sourcing water in tiny houses.
Pipes:
Carry water to fixtures like the kitchen sink and tiny house shower. The bathroom sink is also connected to the overall plumbing system, ensuring seamless integration with other fixtures.
Drainage System:
Waste exits through drain lines.
Hot Water Heater:
Critical for heating water in your tiny home. Locating the hot water heater outside can save space inside a tiny house.
Unique Challenges
Tiny house plumbing is different. Tiny houses have unique plumbing systems that differ from standard residential plumbing due to limited space.
Space is tight.
Everything, including the tank and vent, is smaller.
Many tiny homes are mobile.
Plumbing systems must fit this lifestyle.
Careful planning is a must. Planning the water line layout is crucial to accommodate space constraints and ensure mobility. The complexity of the plumbing system can increase if the tiny house is mobile but adaptability is crucial for different hookups.
Designing an Efficient Plumbing System

Layout Tips
A good layout is key.
It saves space and avoids future issues.
Consider:
Placement of fixtures like bathroom sinks and toilets.
Positioning the shower drain correctly to ensure effective drainage and prevent flooding. Proper drain installation in a tiny house requires ensuring the connections are sloped correctly to avoid clogs.
Space-saving designs.
Sizing Your System
Get the size right.
Think about how many people live in your tiny house.
Match your water tank and water heater to your needs. Selecting the right size water tanks is crucial to ensure you have a reliable water supply, especially if you rely on rainwater collection or need to balance the load for safe travel.
Ensure your system handles water pressure and flow.
Water Supply and Management
Sourcing Options
You have choices for water supply.
Options:
Rainwater collection systems.
City water hookups. Properly connecting to a city’s water line is crucial for ensuring a reliable municipal water supply.
Well systems.
Use a water tank for off-grid living.
Water Filtration and Treatment
Water filtration and treatment are crucial components of a tiny house plumbing system. Since tiny houses often rely on alternative water sources, such as rainwater collection or wells, the water may contain contaminants that need to be removed. A reliable water filtration system can ensure that the water is safe for drinking, cooking, and personal hygiene.
There are several types of water filtration systems available for tiny houses, including:
Activated Carbon Filters: These filters are effective in removing chlorine, lead, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the water.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: This system uses a semipermeable membrane to take out impurities from the water, including dissolved solids, bacteria, and viruses.
Ultraviolet (UV) Light Systems: These systems use UV light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that may be present in the water.
In addition to filtration, water treatment may also be necessary to remove contaminants such as iron, manganese, and hardness minerals. Water treatment systems can include:
Water Softeners: These systems remove hardness minerals from the water, making it softer and more suitable for household use.
Iron and Manganese Removal Systems: These systems use oxidation or ion exchange to remove iron and manganese from the water.
Regular maintenance of the water filtration and treatment systems is essential to ensure that the water remains safe and clean. This includes replacing filters, cleaning the systems, and testing the water quality regularly. By investing in a good water filtration and treatment system, you can ensure that your tiny house plumbing system provides clean and safe water for all your needs.
Water Filtration
Clean drinking water is crucial.
A good water filter makes a difference.
Options:
Simple carbon filters.
Reverse osmosis units.
Consider treating water to remove bacteria and viruses.
Heating Your Water
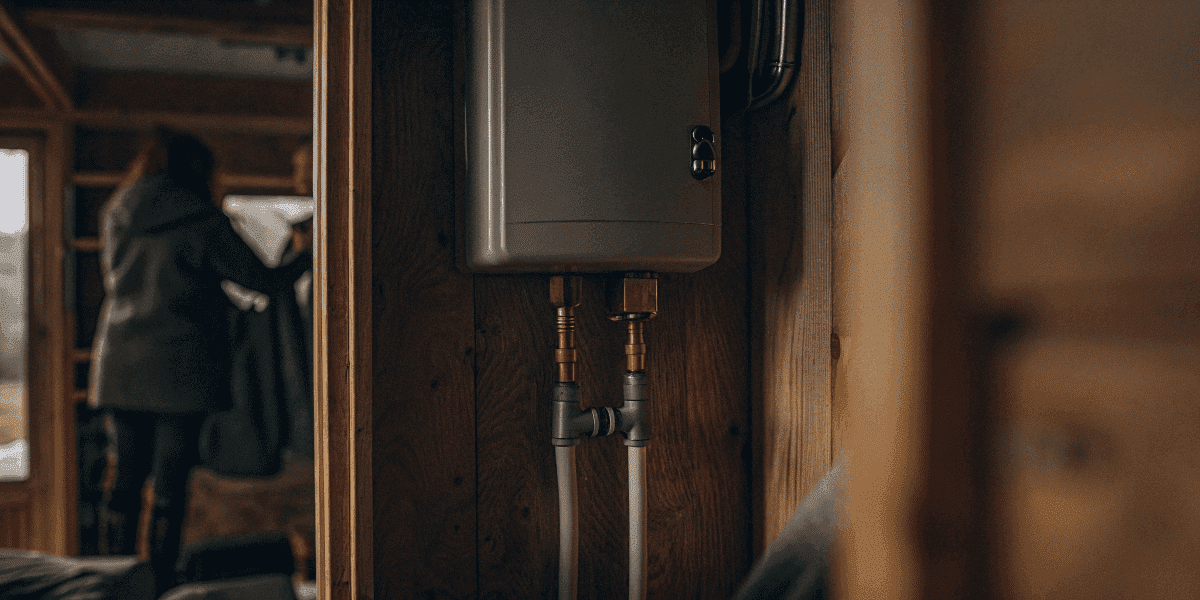
Tankless Water Heaters
Tankless water heaters are great. Tankless water heaters are ideal for tiny homes because they save space and energy by heating water on demand.
They heat water on demand.
They save space and energy.
Perfect for tiny houses.
Traditional Water Heaters
Traditional water heaters are an option too.
They’re cheaper but take up more space.
Pick what’s best for your budget.
Drainage, Venting, and Waste Disposal
Greywater and Blackwater
Tiny homes use less water.
But they still produce greywater and blackwater. Greywater systems filter and reuse water from sinks and showers for non-potable uses like irrigation.
Greywater:
Comes from sinks and showers.
Can be reused or recycled.
Blackwater:
Comes from toilets.
Goes to a septic system or sewer.
Consider a composting toilet to save water. Composting toilets eliminate the need for a connection to sewage and septic systems.
Proper Venting
Venting is vital.
It keeps sewage gases out of your living space.
In Tiny Houses:
An atmospheric vent connects to the main drain line.
Ensure proper venting to avoid clogs and odors.
Choosing the Right Plumbing Materials
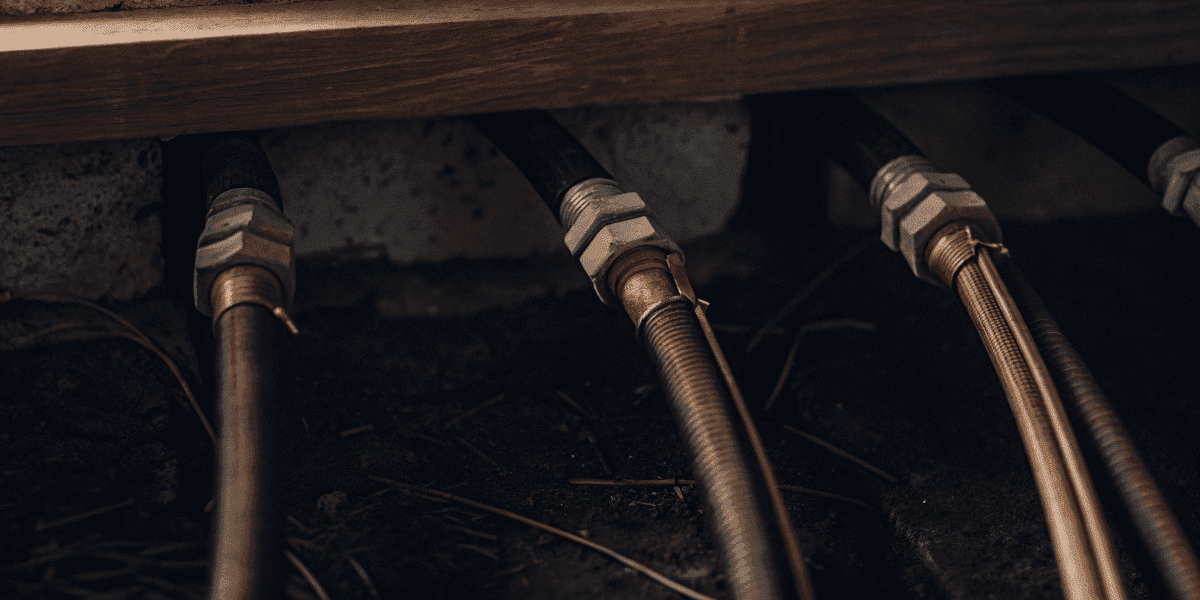
PEX Pipes
PEX pipes are flexible and easy to install. PEX tubing is flexible and can weave through tight spaces without the need for multiple fittings.
They’re great for tiny houses.
Copper Pipes
Copper pipes are durable.
But they’re more expensive and harder to install.
Pick what’s right for your tiny house plumbing system.
Winterizing Your Plumbing
Insulating Pipes
Use foam pipe insulation on exposed pipes. Installing a shut-off valve for the whole house can help manage plumbing issues when the home is unoccupied.
Protect them from freezing temperatures.
Heat Tape
Heat tape keeps pipes warm in cold weather.
Consider a house shut-off valve for emergencies.
DIY vs. Hiring a Pro
DIY Plumbing
DIY can save money.
But know your limits.
Follow local codes.
Hiring a Professional
A pro ensures everything’s up to code.
Good for complex plumbing needs.
Research and hire a reputable plumber.
Essential Tips for Maintenance
Regular Checks
Regular inspections prevent problems. Regular inspections of plumbing systems are necessary to prevent major issues in tiny houses.
Look for leaks and clogs.
Keep a checklist.
Space-Saving Fixtures
Use compact fixtures to save space. Choosing compact fixtures maximizes space utilization in tiny house plumbing designs.
Install them right to avoid issues. Maintaining a good working plumbing system requires regular inspections and access to water lines for repairs.
Estimating Costs
Budgeting
Plumbing a tiny house costs $100 to $200 an hour plus materials. A tiny house plumbing system could range from $1,500 to $4,000, depending on various factors.
Plan your budget.
Compare prices for the best value.
Water-Efficient Fixtures
Water-efficient fixtures save money. Investing in a low-flow toilet or shower head reduces water usage without sacrificing performance in tiny houses.
Low-flow toilets reduce water use.
They’re smart choices for tiny house living.
Protecting from Climate Challenges
Insulate Against Freezing
Insulate pipes in unheated areas.
Use heat tape or cables.
Keep pipes from freezing.
Manage Hot Climates
Managing hot climates is an essential consideration for tiny house plumbing systems. In hot climates, the water demand is higher, and the risk of water scarcity is greater. Here are some tips for managing hot climates:
Use Low-Flow Fixtures: Low-flow showerheads, faucets, and toilets can help reduce water consumption and minimize the risk of water scarcity.
Install a Water-Efficient Hot Water Heater: Tankless water heaters or heat pump water heaters can be more efficient than traditional tank-style water heaters, especially in hot climates.
Use a Greywater System: Greywater systems can help reduce the amount of wastewater generated by the household and can also provide a source of water for irrigation and flushing toilets.
Insulate the Plumbing System: Insulating the plumbing system can help reduce heat gain and minimize the risk of pipes bursting due to high temperatures.
Use Heat-Resistant Materials: Using heat-resistant materials, such as PEX tubing, can help minimize the risk of pipes bursting due to high temperatures.
By following these tips, tiny house owners can manage hot climates effectively and ensure that their plumbing system remains functional and efficient. Proper planning and the right materials can make a significant difference in maintaining a reliable tiny house plumbing system, even in the hottest conditions.
Final Thoughts
A well-planned plumbing system is key for tiny house life.
Use these tips to make your tiny house plumbing work.
Keep it simple and efficient. Tiny house plumbing systems are all about maximizing space and resources while ensuring functionality. By understanding the basics and planning carefully, you can create a plumbing system that meets your needs without compromising on comfort or convenience.
FAQ’s
How do I maintain and protect tiny house plumbing in different climates?
Regular inspections, using insulation, heat tape, and appropriate materials like PEX pipes help prevent freezing in cold climates and manage heat in hot climates.
What are the options for water supply in tiny houses?
Water can be supplied through city hookups, rainwater collection, or well systems, with water tanks used for off-grid living.
How can I design an efficient plumbing system in my tiny house?
Effective design involves careful layout planning, proper sizing of components, space-saving fixture placement, and ensuring reliable drainage and water supply.
What are the main challenges of tiny house plumbing?
Challenges include limited space, the need for smaller components, and the requirement for the system to be adaptable, especially for mobile tiny homes.
How does plumbing work in tiny houses?
Tiny house plumbing involves a water source, pipes, and a drainage system, with options for on-grid or off-grid setups, including rainwater collection.