Deciding between a Tiny House vs Park Model home? We’ll break down their differences in cost, mobility, space, and lifestyle impact to help you choose the best fit.
Key Takeaways
Park model homes are classified as RVs, offering a compact, mobile living solution with stricter construction standards that can simplify financing and insurance.
Tiny houses prioritize customization and sustainability, catering to individuals looking for a minimalist lifestyle, but face regulatory challenges that can complicate placement.
Cost-wise, park model homes may offer a better return on investment due to lower prices and easier financing, while tiny houses appeal to eco-conscious buyers willing to navigate their higher costs.
Understanding Park Model Homes
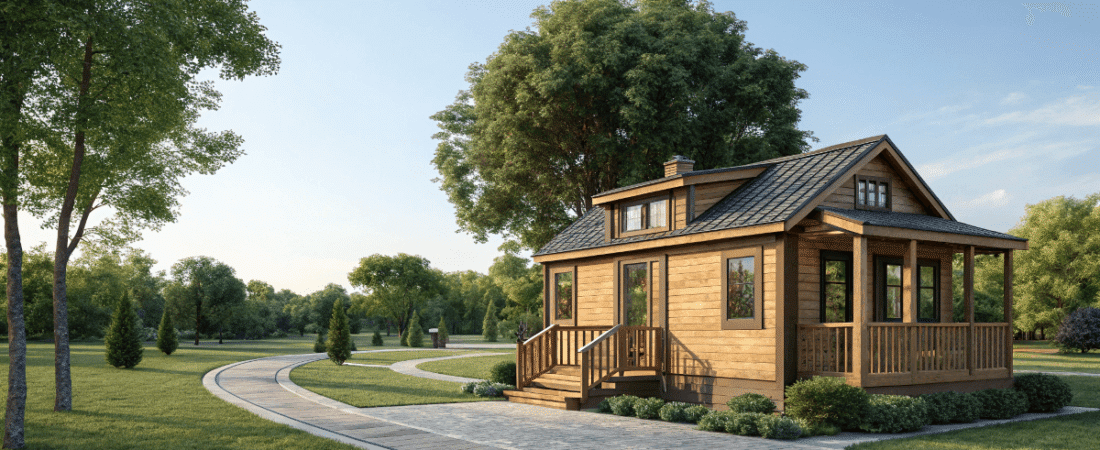
Park model homes are a fascinating segment of the tiny homes market, often misunderstood due to their classification and usage. Unlike traditional tiny houses, park model homes are classified as recreational vehicles (RVs) and are subject to specific regulations and standards. They are typically limited to a maximum of 400 square feet and a width of up to 12 feet, making them compact yet comfortable.
These homes are primarily used in vacation spots or RV parks, offering a unique blend of mobility and stability. Think of them as a hybrid between a traditional mobile home and a tiny house. If you’re considering a park model home, understanding their construction standards, benefits, and drawbacks is crucial to making an informed decision.
Construction Standards of Park Model Homes
One of the key aspects of park model homes is their adherence to ANSI A119.5 standards, which set the safety and quality benchmarks for RVs. This compliance ensures that park model homes are built to a specific set of standards, guaranteeing safety and reliability for their occupants. Each unit must display an RVIA seal, confirming that it meets these stringent safety and quality requirements. This is a significant advantage over many tiny houses, which may not always adhere to local building codes.
The stringent standards applied to park model homes mean that they are recognized as RVs, which influences their pricing and financing options. This classification can make it easier to secure loans and insurance, adding a layer of financial security for potential buyers.
Benefits of Park Model Homes
Park model homes come equipped with modern amenities that rival those of traditional homes, enhancing both comfort and livability. Imagine having a cozy, stylish space complete with all the conveniences you need, from full-sized appliances to high-quality finishes like LP Smartside siding and residential furniture. These homes are not just about compact living; they are about living well within that compact space.
Moreover, park model homes are a cost-effective investment. They offer a low-cost, high return on investment opportunity, making them an attractive option for those looking to maximize their dollars. For example, the Pocono Park Model Home combines a modern design with a rustic vibe, providing a stylish yet comfortable living space.
Drawbacks of Park Model Homes
Despite their many advantages, park model homes do have some drawbacks. The most significant limitation is their space. With a maximum of 400 square feet, these homes can feel cramped, especially for long-term living. This limited space can restrict functionality and make them less suitable for those who need more room to accommodate their lifestyle.
Exploring Tiny Houses
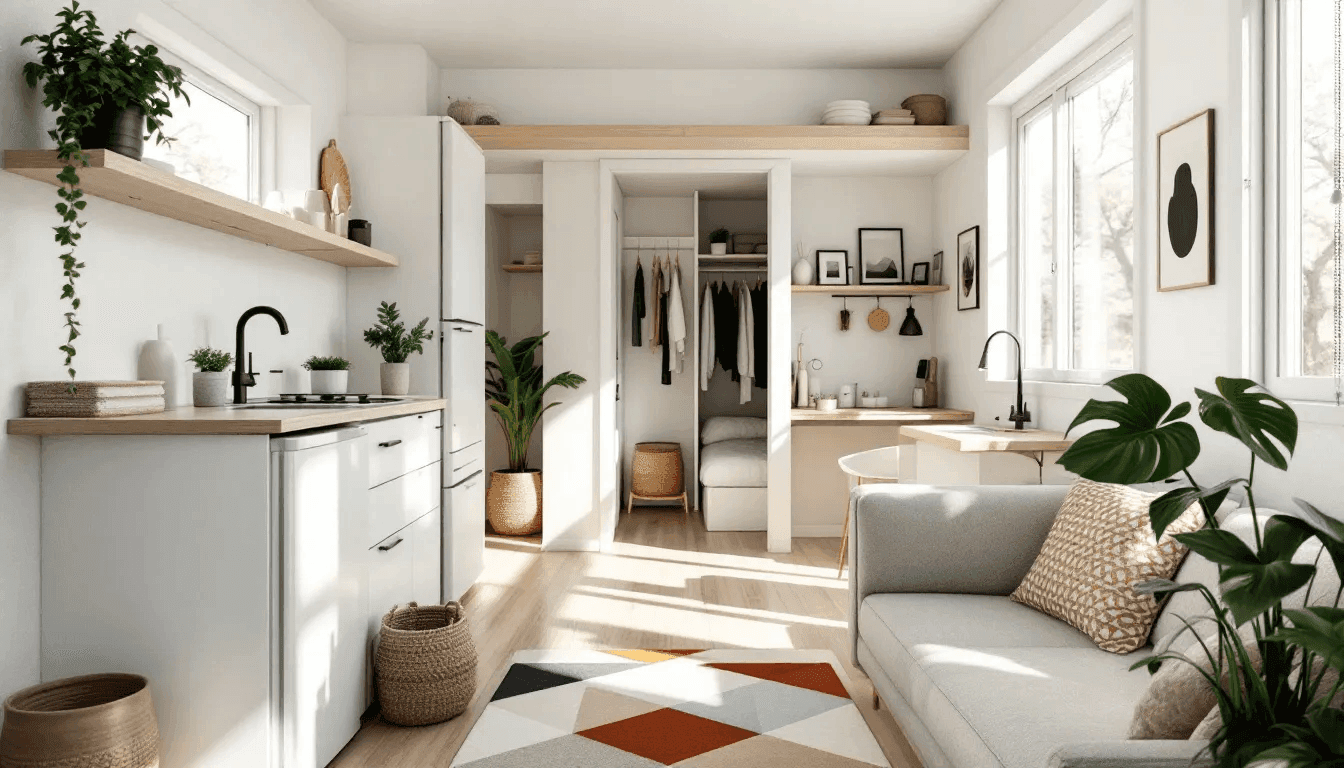

Tiny houses represent a different approach to compact living solutions. Designed for full-time living, these small homes provide an alternative housing option with a smaller footprint. They are eco-friendly, often incorporating sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies, which align with a minimalist lifestyle. The tiny home movement can be a perfect fit for those seeking simplicity.
Tiny houses offer extensive customization options, allowing for innovative designs that cater to individual needs. This flexibility is one of the most appealing aspects of tiny living, but it also comes with its own set of challenges, including regulatory hurdles, zoning restrictions, and very few tiny homes.
Customization and Design Flexibility
The beauty of tiny houses lies in their customization and design flexibility. Owners can tailor their tiny homes to match their unique lifestyles, incorporating features like built-in storage, multi-functional furniture, and personalized decor. Whether you dream of a minimalist retreat or a cozy, eclectic space, tiny houses can be designed to reflect your personal style and needs.
From innovative layouts to creative use of space, the possibilities are endless. Imagine a tiny house with a loft space, a fold-out dining table, and hidden storage compartments – all designed to make the most of every square inch. This level of personalization is one of the main attractions of the tiny house movement.
Regulatory Challenges for Tiny Houses
However, the journey to tiny living is not without its hurdles. Zoning laws and local building codes can complicate where tiny houses can be placed, limiting available land. In some areas, tiny houses are designated as accessory dwelling units (ADUs) or are restricted to RV parks, making it challenging to find suitable locations.
Many tiny houses do not conform to traditional building codes for permanent residences, which can hinder their acceptance and placement. This non-compliance with local laws and local building code regulations often necessitates securing appropriate permits and navigating complex legal barriers, adding another layer of difficulty to the tiny living experience.
Benefits of Tiny Houses
Despite these challenges, tiny houses offer numerous benefits that make them an attractive option for many. They are designed to minimize environmental impact, often using sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies. This leads to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint, aligning with the goals of a minimalist lifestyle.
Living in a tiny house encourages a simpler way of life, focusing on experiences and relationships rather than material possessions. The design of tiny houses often includes multi-functional spaces, fostering a more efficient and decluttered living environment. This simplicity can lead to increased personal satisfaction and happiness, as residents have more time to invest in what truly matters, embracing minimalist living.
Drawbacks of Tiny Houses
On the flip side, the limited space in tiny houses can pose significant challenges. With sizes generally ranging from 400 to 1000 square feet, accommodating personal belongings and maintaining comfort can be difficult, especially for families with children.
This constraint can significantly impact the lifestyle and comfort of its residents.
Cost Comparison Between Park Model Homes and Tiny Houses
When it comes to cost, both park model homes and tiny houses offer unique advantages. Park model homes provide a high return on investment due to their affordability and demand. The average price of a park model home can range from $97,500 to $105,000, depending on the model and location. Financing options for park model homes are generally more accessible, often utilizing RV loans with competitive interest rates.
Tiny houses, on the other hand, can lead to a reduced environmental impact and lower living costs. Their total cost heavily depends on the level of customization and whether the owner undertakes DIY projects. While park model homes can be transported but require special permits, tiny houses often promote sustainability by reducing resource consumption through their minimalistic design.
Placement and Mobility
Placement and mobility are crucial factors to consider when choosing between park model homes and tiny houses. Park model homes are often more accepted in RV parks due to their classification as RVs, whereas tiny houses may not meet RV standards, making their placement more challenging.
While tiny houses are ideally located on private land or as accessory dwelling units (ADUs), they face regulatory challenges. Mobility varies significantly; tiny houses are often built on trailers for easier transport, whereas park models are usually set up in a semi-permanent location and require permits for movement.
Relocating Park Model Homes
Park model homes are classified as park model rvs, which facilitates their mobility and relocation. This built-in mobility feature allows park model homes to be relocated easily without extensive planning, making them a flexible option for those who might want to move their home to different locations, such as an rv park.
However, it’s important to note that relocating a park model home often requires permits and professional assistance due to their size. This adds an extra layer of planning but ensures that the process is done safely and efficiently.
Moving Tiny Houses
Moving tiny houses involves a different set of challenges. Transporting these homes can involve complex logistics and safety measures, making relocation more challenging than with park model homes. The risk of rolling over due to their design necessitates specialized transport equipment to ensure safety.
Additionally, careful preparation is needed to secure appliances and furniture to prevent damage during transit. This makes the process of moving a tiny house more involved and potentially more costly.
Lifestyle Considerations
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in deciding between park model homes and tiny houses. Park model homes are classified as recreational vehicles designed primarily for long-term or permanent placement, often serving as vacation or retirement homes. They are typically set up with all necessary utilities, providing a comfortable living experience.
On the other hand, tiny houses are designed for full-time living, promoting a minimalist lifestyle that focuses on experiences and relationships rather than material possessions. Family dynamics and recreational needs significantly impact the decision between these two options.
Vacation vs. Full-Time Residence
Park model homes are primarily utilized for vacation purposes, providing a temporary yet comfortable living space. They are typically designated for seasonal or recreational use in campgrounds or similar locations, making them ideal for those who need a getaway spot with a park model RV.
In contrast, tiny houses are generally designed for year-round living. They can be intended for either temporary or permanent residence, making them a versatile option for those looking to downsize their living space.
The choice between park model homes and tiny houses often hinges on lifestyle preferences, such as usage frequency and family dynamics.
Space and Comfort
When it comes to space and comfort, park model homes generally provide more spacious interiors compared to tiny houses. With more square footage and features like lofts and modern amenities, park model homes offer a higher level of comfort for their occupants.
Tiny houses, on the other hand, prioritize minimalism and efficient use of smaller areas. While they may lack the spaciousness of park model homes, they promote a decluttered and efficient living environment that aligns with a minimalist lifestyle.
Financing Options
Financing options for park model homes and tiny houses differ significantly, reflecting their unique classifications. Park model homes, being classified as recreational vehicles, can be financed through various loan types, including personal unsecured or secured loans, RV loans, and manufactured home loans. RV loans, in particular, offer competitive interest rates similar to auto loans and typically span 10 to 20 years, although they may have higher rates than traditional mortgages.
On the other hand, financing tiny houses can be more challenging. Since they are not always classified as traditional homes, securing a mortgage can be difficult. Personal loans and RV loans are often the best bet for financing tiny houses, but they come with shorter terms and higher interest rates.
Improving your credit score can lead to better loan terms and interest rates, making it easier to finance your tiny living dream.
Resale Value
The resale value of park model homes and tiny houses is influenced by various factors, including market trends, construction quality, and location. The market for park model homes has been expanding, suggesting a promising future for their resale values due to increased popularity. Younger buyers and advancements in construction quality are enhancing the resale potential of park models.
Well-maintained park model homes in desirable areas retain their value more effectively than those in less attractive locations. The overall condition and the quality of materials used in construction play a significant role in determining resale value. High-quality materials ensure that park model homes maintain their value better, providing a solid return on investment for owners.
Key Differences at a Glance
When comparing park model homes and tiny houses, several key differences stand out. Park model homes are typically under 400 square feet and classified as RVs, which makes them easier to comply with regulations and relocate. In contrast, tiny houses can range from under 400 to 1000 square feet and often face regulatory challenges due to their unique design and lack of official classification.
Park model homes are mainly made for temporary use, like vacations. In contrast, tiny houses are typically designed for people to live in full-time. This distinction influences not only their design but also their placement and mobility. Park model homes benefit from ease of relocation due to their RV classification, while moving tiny houses involves complexities and specialized equipment.
Summary
Deciding between a tiny house and a park model home ultimately depends on your lifestyle, budget, and long-term goals. Park model homes offer modern amenities, easier financing options, and are ideal for vacationing or seasonal living. They provide a comfortable and stylish living space with a high return on investment.
Tiny houses, on the other hand, promote sustainability and a minimalist lifestyle, making them perfect for year-round living. They offer extensive customization options and lower utility costs but come with regulatory challenges and space constraints. By weighing the benefits and drawbacks of each, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs and aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between park model homes and tiny houses?
Park model homes are generally classified as RVs and are typically under 400 square feet for vacation use, while tiny houses can range from under 400 to 1000 square feet and are designed for full-time living, often facing stricter regulations. So basically, if you want something more like a getaway, opt for a park model; for a permanent solution, go for a tiny house.
Can I finance a park model home like a regular house?
You can’t finance a park model home like a regular house because they’re considered RVs. Instead, look into RV loans, personal loans, or manufactured home loans, but be prepared for shorter terms and potentially higher interest rates.
Are tiny houses more eco-friendly than park model homes?
Absolutely, tiny houses tend to be more eco-friendly because they usually use sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies, which helps cut down on environmental impact and utility costs.
What are the challenges of moving a tiny house?
Moving a tiny house can be quite tricky because it involves careful planning to secure all your belongings, plus you need specialized transport equipment to keep everything safe during the move. It’s definitely more complicated than just relocating a typical park model home.
Which option is better for long-term living?
Tiny houses are better for long-term living because they are designed for year-round occupancy and can be extensively customized. Park model homes are more suitable for short-term stays.



