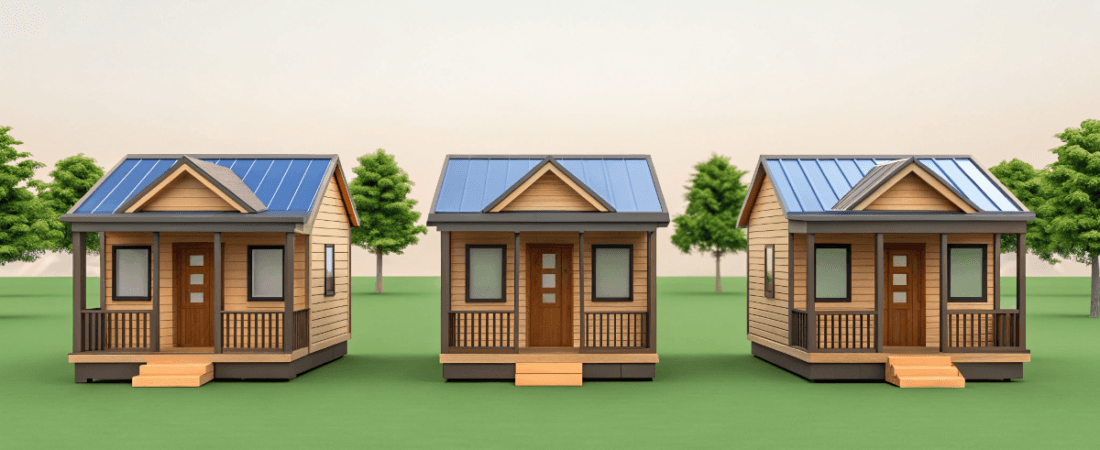
Low income tiny homes offer a cost-effective housing solution for families struggling with high living costs. These small, affordable homes provide a pathway to stable housing. This article details the advantages of low income tiny homes, including their design, financing options, and their impact on communities.
- Key Takeaways
- Low Income Tiny Homes: Affordable Living Solutions
- Introduction
- Addressing Housing Affordability
- Design and Space Efficiency
- Sustainable Building Materials
- Financing Options for Tiny Homes
- Community Support and Resources
- Legal Considerations and Zoning Laws
- Non-Profit Initiatives
- Impact on Homelessness
- Urban Strategies for Tiny Homes
- Customization and Personalization
- Economic Benefits
- Learning Opportunities
- Portability and Flexibility
- Smart Technology Integration
- Eco-Friendly Accommodations
- Legislative Developments
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
The Tiny Homes project in Detroit provides affordable housing for low-income individuals through a rent-to-own model, making homeownership attainable within seven years.
Tiny homes address housing affordability and reduce homelessness by offering compact, sustainable living solutions that incorporate innovative designs and community support.
Recent legislative developments and modifications to zoning laws enhance the viability of tiny homes, promoting diverse and affordable housing options across various municipalities.
Low Income Tiny Homes: Affordable Living Solutions
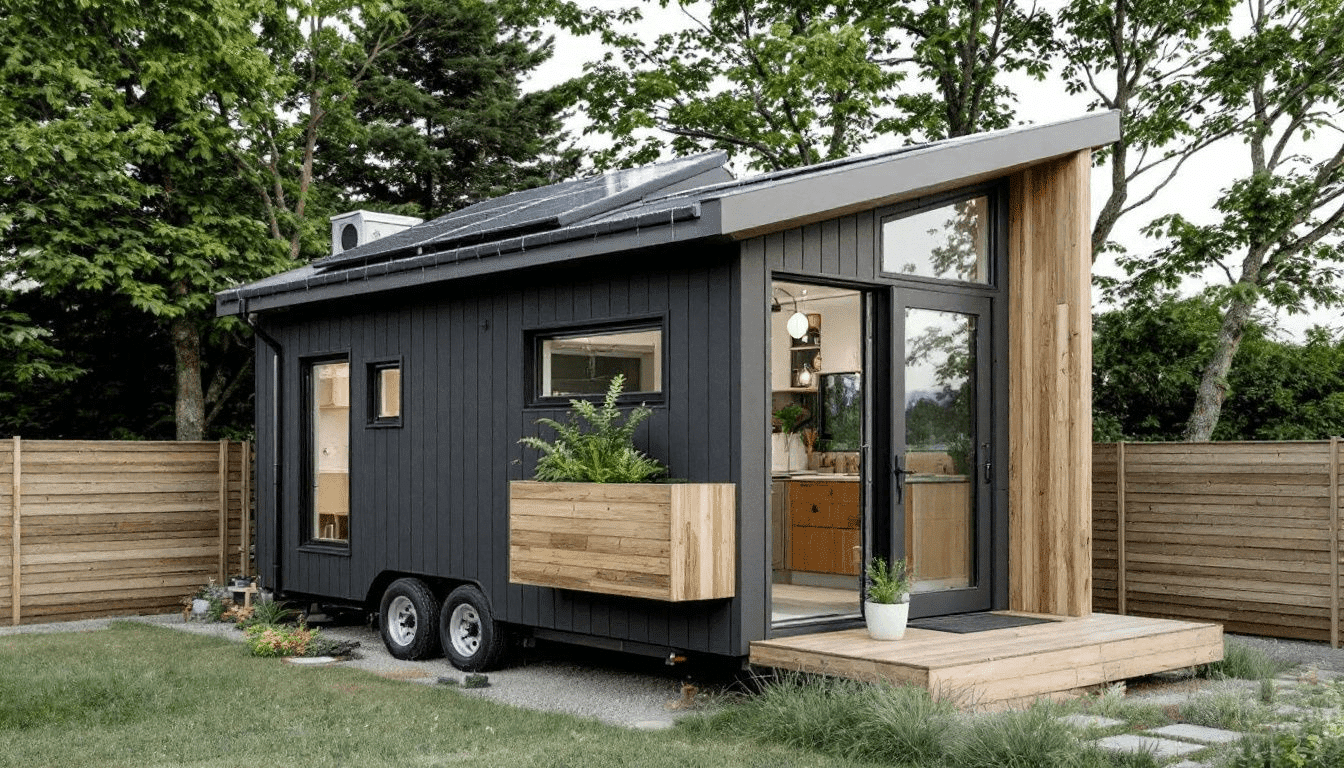

The Tiny Homes project in Detroit is a prime example of how tiny homes can serve as a lifeline for low-income individuals. This initiative aims to alleviate asset inequality by providing affordable housing options for people earning as little as ,000 annually.
Through a rent-to-own model, tenants can own their homes after seven years, making homeownership attainable for low-income families. These tiny homes, ranging from 250 to 400 square feet, are thoughtfully designed to offer compact yet comfortable living spaces, complete with features like front porches or rear decks to enhance the living experience, including options for a small house.
Introduction
Low-income tiny homes provide a practical response to the rising housing costs that burden many individuals and families. These small houses offer a cost-effective option that eases the pressure on low-income households, making stable housing more accessible. By targeting the core of the housing crisis, tiny homes offer a viable alternative for those facing housing challenges.
In addition to providing shelter, tiny homes significantly reduce homelessness. Non-profit initiatives have been crucial in creating tiny home villages that offer both homes and supportive services to help residents thrive.
These communities are crafted to offer a holistic living environment, providing resources and support to help individuals rebuild their lives and aspire to a brighter future.
Addressing Housing Affordability
Low-income tiny homes serve as a beacon of hope in addressing housing shortages. They provide an affordable option for individuals and families, enabling even those earning as little as $8,000 annually to find a place to call home. By boosting the overall supply of housing, tiny homes alleviate market pressure and offer a budget-friendly alternative for low-income families.
A standout feature of tiny homes is the rent-to-own model, enabling tenants to own their homes after a period, usually seven years. This approach not only provides affordable housing but also creates a pathway to homeownership, often unattainable for low-income families.
Innovative designs, including features like porches or decks, enhance the living experience, making tiny homes a desirable option. Additionally, sustainable developments, such as solar power usage, reduce utility costs for residents, making these homes even more affordable.
Design and Space Efficiency
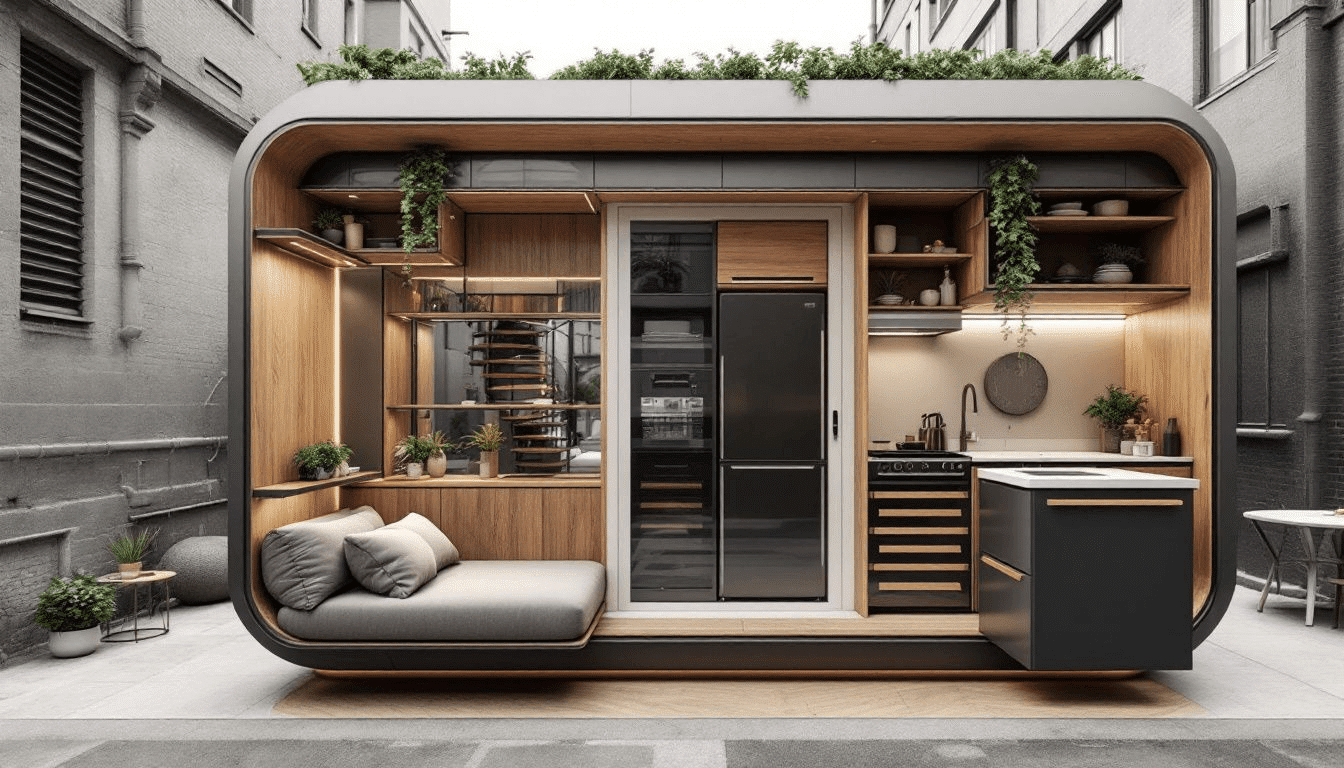
Tiny homes are designed with remarkable space efficiency. Incorporating multifunctional furniture and creating multi-purpose rooms maximize the utility of every square foot. For instance, a single room can serve as a living area, dining space, and office, thanks to clever design features like pull-out desks and convertible furniture. Open floor plans further enhance the sense of space, making these compact homes feel larger.
Sliding doors save valuable space compared to traditional swing doors, and open storage solutions reduce the need for bulky cabinets. Vertical surfaces are utilized for shelving, adding both storage options and aesthetic value.
Large windows and the use of translucent materials let natural light flood the interior, creating a bright and inviting living space. Hidden storage in unconventional spaces, like under stairs, also contributes to the efficient use of space in tiny homes.
Sustainable Building Materials
Sustainability is central to tiny home construction. Many are built using materials like bamboo flooring, natural paints, and recycled metal roofing, enhancing durability and reducing environmental impact. Solar panels and energy-efficient appliances not only promote long-term financial savings but also help lower utility costs for residents.
Emphasizing sustainability in their design, tiny homes have a lower environmental footprint, making them a responsible choice for eco-conscious individuals.
Financing Options for Tiny Homes

Financing a tiny home can be more accessible than traditional housing. Various options, including personal loans, crowdfunding, grants, and RV loans, offer aspiring tiny home owners flexibility to choose a solution that fits their financial situation best.
Personal Loans
Personal loans are popular for financing tiny homes due to their flexibility. Banks, credit unions, and online lenders offer loans specifically for tiny home purchases.
A key advantage of personal loans is their use for various expenses related to tiny home construction and purchase, providing financial freedom to the borrower.
Crowdfunding and Grants
Crowdfunding and grants have emerged as effective ways to finance tiny home projects. Platforms like Kickstarter enable individuals to raise funds for their tiny home endeavors by appealing to a community interested in sustainable living. Additionally, grants focused on eco-friendly housing solutions support low-income families.
Application processes for some programs, like the Tiny Homes program, open at specific times, providing opportunities for those in need to secure funding.
RV Loans
RV loans are tailored for mobile tiny homes, offering a unique financing option for those wishing to live on wheels. Lenders treat tiny homes as RVs if they meet certain criteria, with loans structured similarly to auto loans, often requiring a down payment.
Shopping around for the best RV loan deal is advisable, as terms and interest rates can vary significantly between lenders.
Community Support and Resources
Tiny home communities offer a unique blend of affordability, community, and freedom. Co-housing communities, where amenities are shared, foster camaraderie and friendship among residents. People in these communities often pursue a lifestyle of simplicity and affordability, aligning perfectly with the principles of tiny home living. Joining the tiny house community allows residents to enjoy flexibility and greater community involvement.
Online communities also support tiny home enthusiasts significantly. Forums and social media groups offer platforms for sharing advice, resources, and inspiration, helping individuals navigate the challenges and joys of tiny home living.
Crowdfunding platforms can be instrumental in raising funds for tiny home projects, allowing the community to support sustainable living initiatives. This combination of community support and online resources creates a nurturing environment for those pursuing low-income tiny home living.
Legal Considerations and Zoning Laws
Understanding local zoning laws is crucial for tiny home living. Zoning regulations determine where you can legally place your tiny home, and these laws vary significantly between communities. Research and patience are needed to find a legal spot for a tiny home, as the process can be complex and time-consuming.
Fortunately, many communities are adjusting their zoning regulations to embrace tiny home developments. Workshops and educational programs often cover building techniques and zoning challenges, helping prospective tiny homeowners navigate the legal landscape. This shift reflects a broader recognition of the need for diverse and affordable housing options.
Non-Profit Initiatives
Non-profits significantly contribute to developing affordable tiny home solutions. Their efforts are crucial in addressing housing needs. These organizations often lead the way in building tiny home villages for the homeless, providing secure and supportive living environments. Some non-profits offer grants specifically aimed at supporting low-income housing projects, further expanding these initiatives.
Cass Community Social Services is a notable example, constructing 25 tiny homes in Detroit, each on a designated lot. Residents are primarily low-income individuals who have faced homelessness, incarceration, or aging out of the foster system. Initially, residents rent their tiny homes for one year, with a pathway to homeownership available after seven years.
These homes are built by trained professionals and volunteers, fostering a sense of community and shared purpose. Initiatives like Pivot provide essential life skills training, helping residents achieve long-term success.
Impact on Homelessness

Tiny homes have a significant positive impact on reducing homelessness. The Tiny Homes project in Detroit aims to alleviate asset inequality by providing affordable housing options for low-income individuals, including those previously homeless or aged out of the foster care system. Tiny home villages serve as effective emergency or affordable housing solutions for those experiencing homelessness.
Organizations like Community First! Villages and Operation Tiny Home provide access to essential services such as healthcare, workshops, and job training programs. These organizations aim to help individuals experiencing homelessness, veterans, elders in need, disaster survivors, and at-risk populations.
The design of tiny home communities fosters a sense of belonging and support, aiding residents’ transition towards permanent housing. Outcomes observed with tiny homes include reductions in homelessness and increased stability for at-risk populations.
Urban Strategies for Tiny Homes

Urban strategies for integrating tiny homes are evolving as cities recognize the need for more flexible housing solutions. Many municipalities are amending their zoning laws to support tiny home construction, allowing for more diverse and affordable housing options. Cities like Ann Arbor and Detroit have made provisions in their zoning codes to support tiny house living, reflecting a broader commitment to sustainable, affordable housing solutions.
Specific examples in Michigan show how local zoning laws can impact tiny home placement. Certain counties, such as Montmorency, have modified their regulations to facilitate tiny home developments. While Detroit has strict regulations regarding auxiliary residences, suburban areas offer greater flexibility for tiny home living.
These zoning regulation adjustments are crucial for encouraging the development of tiny home communities and addressing housing shortages.
Customization and Personalization
One of the most appealing aspects of tiny homes is their adaptability and customization options. They can be tailored to meet various household needs, including special needs, making them a popular choice. Owners can select materials and layouts that resonate with their personal style, creating a living space that reflects their values and preferences.
Options like eco-friendly materials and multifunctional spaces further enhance tiny homes’ customization potential.
Economic Benefits
The economic benefits of living in tiny homes are substantial. Here are some key advantages:
Natural daylight from large windows and skylights reduces the need for artificial lighting, leading to lower electricity bills.
Implementing rainwater harvesting systems minimizes reliance on municipal water sources, further reducing utility expenses.
Multi-layered insulation improves thermal performance and lowers energy costs, contributing to significant savings on heating and cooling.
These factors collectively contribute to a more sustainable and cost-effective lifestyle.
Other financial benefits include cross-ventilation strategies that naturally cool homes, reducing the need for air conditioning and its associated expenses. Tiny homes generally require less maintenance due to their small footprint, leading to lower long-term ownership costs. These cost-saving measures make tiny homes economically viable for many.
Learning Opportunities
Learning opportunities abound for those interested in tiny homes. Workshops and expos provide valuable insights into design, construction, and maximizing small spaces. For example, a workshop in Ann Arbor attracted around 100 participants interested in building their own tiny homes. Local Facebook groups and other online communities also offer support and knowledge-sharing opportunities for those looking to embark on their tiny home journey.
The tiny house movement has even been integrated into university architecture classes, offering students hands-on experience in design and construction.
Portability and Flexibility
One of the key advantages of tiny homes is their portability and flexibility. Tiny homes on wheels offer the freedom to move without leaving the home behind, allowing owners to experience various living environments. This mobility enables a living experience that adapts to different locations, providing personal freedom and a connection to one’s belongings.
Smart Technology Integration
Smart technology integration in tiny homes enhances the living experience by increasing efficiency and comfort.
Features include:
Smartphone-controlled lighting
Temperature control systems
Security systems that allow residents to manage their homes with ease
Automated coffee makers
Smart thermostats that improve daily convenience and overall comfort.
Smart thermostats, in particular, adjust the temperature based on residents’ habits, leading to lower energy bills and a reduced environmental impact. Intelligent storage solutions also optimize space and organization, further enhancing the functionality of tiny homes.
Eco-Friendly Accommodations
Tiny home hotels serve as eco-friendly accommodations that offer an alternative to traditional lodging. These hotels often feature unique designs and personalized experiences, providing guests with a tranquil environment surrounded by nature.
Staying in a tiny home hotel allows guests to enjoy the serenity of picturesque settings, enhancing relaxation and connection to the outdoors.
Legislative Developments
Recent legislative developments have made tiny homes more legally viable. In Michigan, legislators have introduced a new category of residence called ‘Economy Efficient Dwelling’ to accommodate tiny homes. The state has been proactive in creating a framework that allows for different types of tiny homes, including both permanent and temporary structures.
Nationwide, there is hope that easing of zoning restrictions will support the growing trend of tiny home living.
Summary
Tiny homes offer a viable solution to the housing crisis, providing affordable, sustainable, and flexible living options. From their innovative design and space efficiency to their economic benefits and community support, tiny homes address many challenges faced by low-income individuals and families. The rent-to-own models and various financing options make homeownership attainable, while the emphasis on sustainability reduces environmental impact and utility costs.
The impact of tiny homes on reducing homelessness is profound, offering stable housing and supportive communities for those in need. With ongoing legislative developments and urban strategies, the future of tiny homes looks promising. As more people embrace this lifestyle, the tiny home movement will continue to grow, providing a beacon of hope for affordable housing solutions. Whether you’re considering downsizing, looking for an eco-friendly living space, or seeking a supportive community, tiny homes offer endless possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How affordable are tiny homes for low-income individuals?
Tiny homes are quite affordable for low-income individuals, with options such as rent-to-own models and diverse financing solutions available for those earning as little as $8,000 annually. This approach significantly enhances accessibility to housing for this demographic.
What are the main benefits of living in a tiny home community?
Living in a tiny home community provides affordability and a strong sense of community, while also granting access to shared amenities. This arrangement encourages a lifestyle focused on simplicity and mutual support.
How do tiny homes contribute to reducing homelessness?
Tiny homes significantly contribute to reducing homelessness by offering stable housing and supportive environments for vulnerable populations, including those transitioning from foster care or incarceration. This approach fosters stability and community integration for individuals in need.
What are some common financing options for tiny homes?
Common financing options for tiny homes include personal loans, crowdfunding, grants, and RV loans, which provide varying terms and flexibility to suit different needs.
Are there legal challenges to placing a tiny home?
There are legal challenges to placing a tiny home, primarily due to varying local zoning laws. It is essential to research and understand these regulations, although some communities are beginning to adapt their laws to facilitate tiny home developments.



